Diffusion Probabilistic Models For 3d Point Cloud Generation
Diffusion Probabilistic Models For 3D Point Cloud Generation
3D point clouds are a digital representation of physical objects. They are used in many fields such as computer vision, robotics, and virtual reality. A point cloud is a collection of points in three-dimensional space. Each point is represented by its x, y, and z coordinates. These points can be used to create a 3D model of an object or a scene.
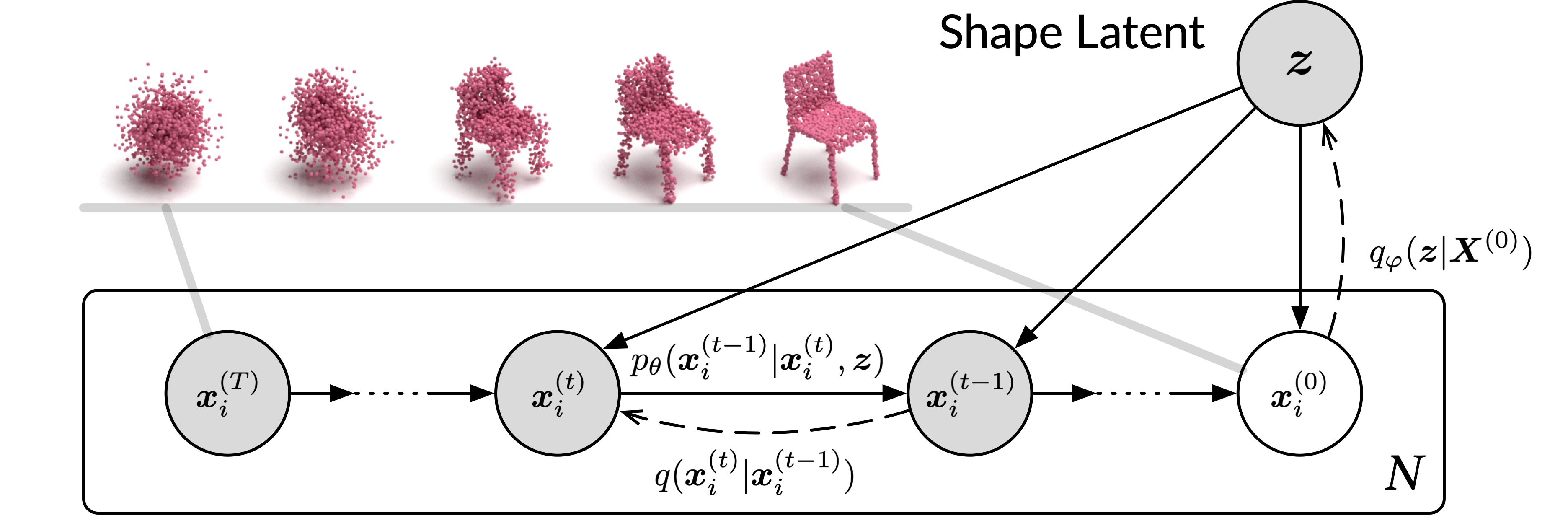
Diffusion Probabilistic (DP) models are a type of probabilistic model used to generate 3D point clouds. These models use a process known as diffusion to generate points on a 3D surface. Diffusion is a stochastic process that models the spread of particles over a surface. The DP model uses a set of parameters to control the diffusion process and the final point cloud generated.
How Does Diffusion Probabilistic Model Work?
The DP model works by randomly sampling points on the surface of an object. These points are then used to create a set of directions, called a diffusion field. The diffusion field controls the spread of the points over the surface of the object. The points are then moved in the direction of the diffusion field. As the points move, they interact with each other, forming clusters. These clusters are then used to generate the final 3D point cloud.
Advantages of a Diffusion Probabilistic Model
The DP model has several advantages over other methods of generating 3D point clouds. First, it is a stochastic process, which means that the generated point clouds are unique. This is important in applications such as computer vision and virtual reality, where the exact shape of an object is important. Second, the DP model can generate very large point clouds, which is useful for applications such as robotics or 3D printing.
Limitations of a Diffusion Probabilistic Model
The DP model has some limitations. First, it is computationally expensive. Generating large point clouds can take a significant amount of time. Second, the model is sensitive to the initial point cloud used as input. If the input point cloud is not of high quality, then the generated point cloud may not be accurate. Finally, the model is limited by the diffusion field used. If the field is not precise enough, then the generated point cloud may not be accurate.
Conclusion
Diffusion Probabilistic models are a powerful tool for generating 3D point clouds. They are a stochastic process, so they can generate unique point clouds. They can also generate large point clouds, which is useful for applications such as robotics or 3D printing. However, they are computationally expensive, and are sensitive to the initial point cloud used as input. Therefore, it is important to consider the limitations of the DP model before using it for a particular application.