3d Bohr Model Of Magnesium
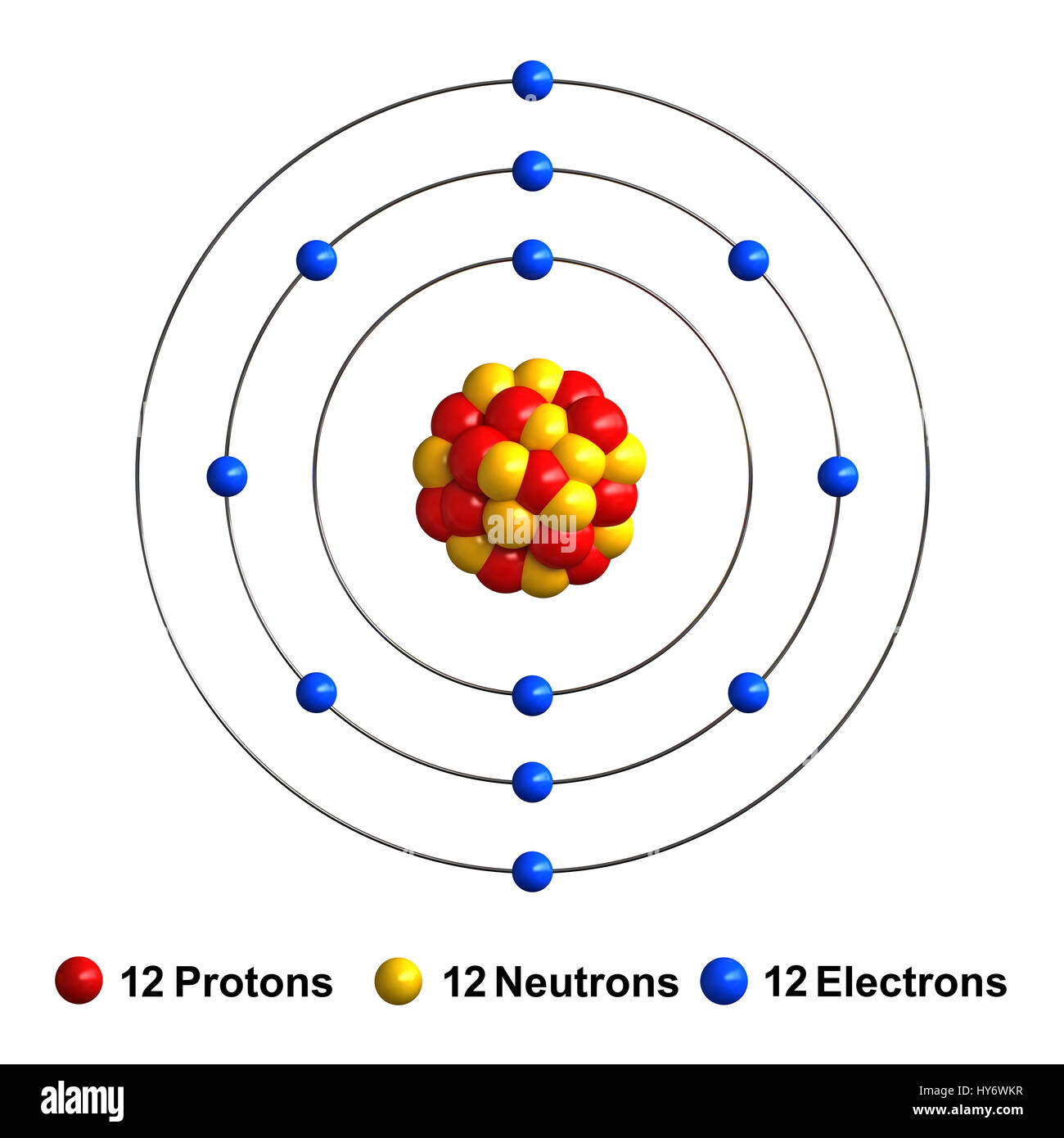
3D Bohr Model Of Magnesium
The Bohr model of the atom is an important concept in the field of Chemistry. It is used to explain the structure and behavior of atomic particles. Magnesium is an element that is an important component of many compounds and materials. Thus, it is important to understand the 3D Bohr Model of Magnesium in order to understand its behavior and characteristics.
Overview of Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element that is found in abundance in nature. It is a silvery-white metal that has a variety of uses in both scientific and industrial applications. Magnesium is an important component of many compounds and materials, such as aluminum alloys, explosives, and fire retardants. Magnesium is also an important component of the human body, where it plays a role in energy production, nerve conduction, and other metabolic processes.
The atomic number of Magnesium is 12, which means that each atom of Magnesium contains 12 protons and 12 electrons. Magnesium is classified as an alkaline earth metal, which means that it is relatively reactive and has a low melting point.
The Bohr Model of Magnesium
The Bohr model of the atom is a model developed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. This model is used to explain the structure and behavior of atoms, and it is based on the idea that electrons are arranged in distinct shells or energy levels around the nucleus. Each shell can contain a certain number of electrons, and the electrons in each shell are arranged in a manner that minimizes the total energy of the atom.
The Bohr model of Magnesium is based on the idea that Magnesium has three shells, each containing two electrons. The outer shell, or the third shell, contains eight electrons, while the inner shells contain two and two electrons respectively. This means that each atom of Magnesium contains twelve electrons in total.
The 3D Bohr Model of Magnesium
The 3D Bohr Model of Magnesium is a visual representation of the Bohr model of Magnesium. This model is used to help visualize the structure of Magnesium atoms and to better understand its behavior and characteristics. The 3D model consists of three concentric circles that represent the three shells of Magnesium. The outermost circle represents the third shell, which contains eight electrons, while the inner circles represent the two inner shells, which contain two electrons each. The circles are connected by arrows to represent the movement of the electrons within the shells.
Applications of the 3D Bohr Model of Magnesium
The 3D Bohr Model of Magnesium can be used to better understand the structure and behavior of Magnesium atoms. It can also be used to explain how Magnesium atoms interact with other atoms in chemical reactions. In addition, the 3D Bohr Model can be used to explain the formation of compounds and materials that contain Magnesium, such as aluminum alloys, explosives, and fire retardants.
The 3D Bohr Model of Magnesium is an important concept in the field of Chemistry and can be used to understand the behavior and characteristics of Magnesium atoms. This model can also be used to explain the formation of compounds and materials that contain Magnesium and to better understand chemical reactions that involve Magnesium atoms.