3d Model Human Body Muscles
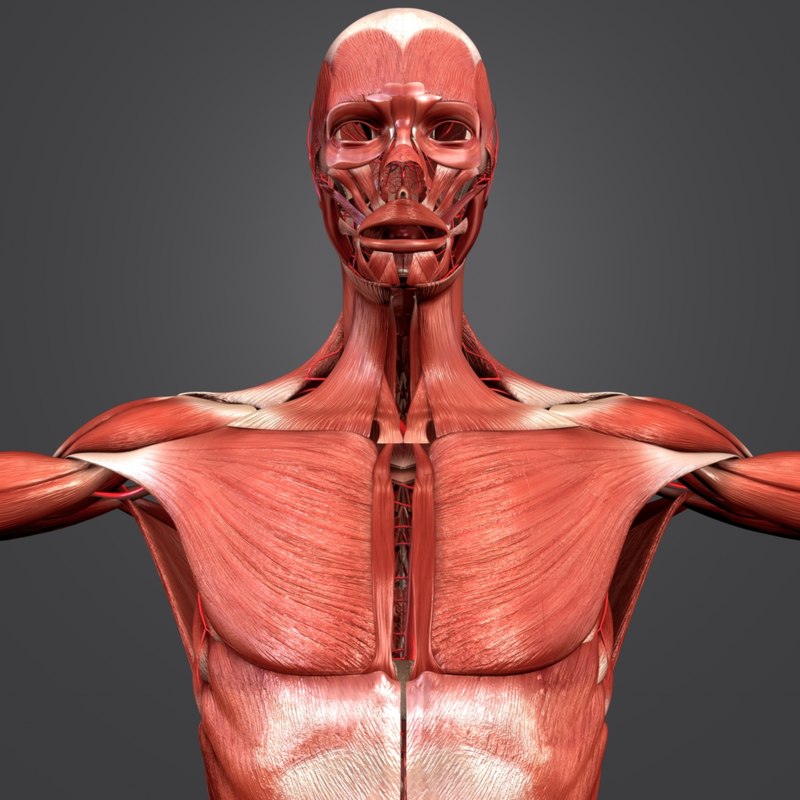
Understanding the Anatomy of Human Body Muscles
The muscles of the human body are incredibly complex, and their purpose is to help us move and perform everyday activities. To understand how muscles work, it is important to understand the anatomy of the human body muscles. The muscles of the human body are divided into three main categories: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. Each of these types has its own unique anatomy and function, and understanding each one can help us better understand how the body works.
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are the most well-known type of muscle in the human body. They are responsible for voluntary movements, and they make up the majority of our body's muscles. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones via tendons, and they are made up of muscle fibers that are arranged in a parallel way. Each skeletal muscle has its own nerve supply, and they are capable of contracting and relaxing in response to nerve impulses.
Structure
Skeletal muscles are made up of bundles of muscle fibers, which are bundled into fascicles. Each fascicle is surrounded by a sheath of connective tissue called the epimysium. This epimysium helps to protect and support the muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber is made up of smaller individual fibers, which are surrounded by a protective cover called the endomysium. The endomysium helps to keep the individual fibers in place and helps to regulate the amount of calcium and other minerals that enter and exit the muscle fibers.
Contraction
When a skeletal muscle contracts, it is because of an electrical impulse that is sent from the brain. This impulse travels down the spinal cord and then to a specific muscle. The impulse then causes the muscle fibers to contract, and this causes the muscle to shorten and become stronger. When the muscle is relaxed, the muscle fibers relax, and the muscle returns to its original length.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles are also known as heart muscles, and they are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the heart. Unlike skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles are not under voluntary control, and they are made up of long, thin fibers that are arranged in a helical pattern. Cardiac muscles have a unique ability to contract and relax without any external stimulation, and this is what helps the heart to pump blood throughout the body.
Structure
Cardiac muscles are made up of elongated fibers that are arranged in a helical pattern and are connected together by intercalated discs. These intercalated discs are made up of proteins and lipids, and they help to keep the cardiac muscle fibers in place. Each cardiac muscle fiber is surrounded by a protective cover called the sarcolemma, and this helps to protect the individual muscle fibers from damage.
Contraction
Cardiac muscles contract in a wavelike manner, and this helps to pump blood throughout the body. The contraction of the cardiac muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, and this helps to regulate the amount of blood that is pumped throughout the body. When the cardiac muscle contracts, it causes the heart to pump blood, and when it relaxes, it causes the heart to fill with blood again.
Smooth Muscles
Smooth muscles are found throughout the body, and they are responsible for involuntary movements. Smooth muscles are made up of short, spindle-shaped fibers, and they are arranged in a circular pattern. Unlike skeletal and cardiac muscles, smooth muscles are not under voluntary control, and they can contract and relax without any external stimulation.
Structure
Smooth muscles are made up of short spindle-shaped fibers that are arranged in a circular pattern. Each smooth muscle fiber is surrounded by a protective cover called the sarcolemma, and this helps to protect the individual muscle fibers from damage. The sarcolemma is made up of proteins and lipids, and it helps to keep the individual muscle fibers in place.
Contraction
Smooth muscles contract and relax in response to nerve impulses, and this helps to regulate the movement of various organs and tissues. The contraction of the smooth muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, and this helps to regulate the amount of blood that is pumped throughout the body. When the smooth muscle contracts, it causes the organ or tissue to move, and when it relaxes, it causes the organ or tissue to return to its original state.
Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body muscles is important for understanding how the body works and how it is able to move and perform everyday activities. Learning about the different types of muscles, their anatomy, and their function can help us better understand the complexities of the human body.